Geocoding
Understanding Geocoding: Turning Locations into Coordinates.
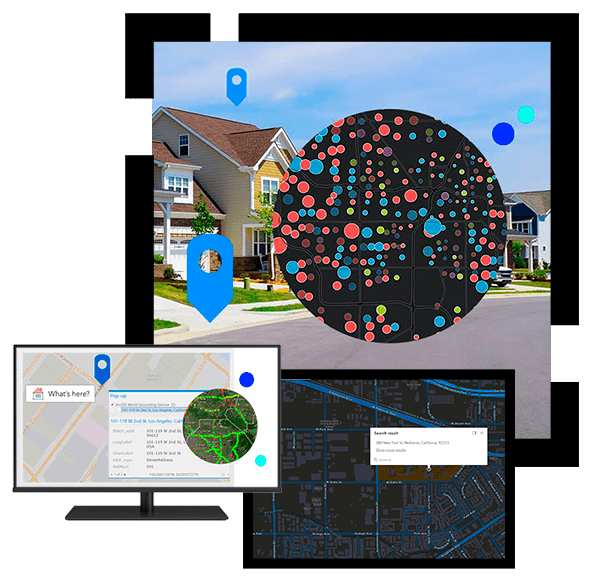
Geocoding is the process of converting addresses, and or place names into points on a map. Using Esri software like ArcGIS Pro, you can take a list of addresses (e.g., customer locations or store sites) and easily pinpoint them on a map as precise coordinates. This makes it simple to visualise where things are, analyse patterns, see context and relationships and make informed decisions based on location. Whether you’re mapping delivery routes, finding the closest services, or studying market trends, geocoding helps transform raw data into actionable insights.
Why Geocode?
Geocoding transforms human readable location data ( address) into actionable insights by converting addresses or place names into precise map points. This enables organisations to visualise and analyse spatial relationships, optimise operations, and make informed decisions. With tools like Esri’s ArcGIS software suite, geocoding enhances efficiency by streamlining processes such as route planning, service delivery, and market analysis. It empowers businesses to uncover trends, improve customer engagement, and gain a competitive edge through accurate, location-based intelligence.
Geocoding as a solution
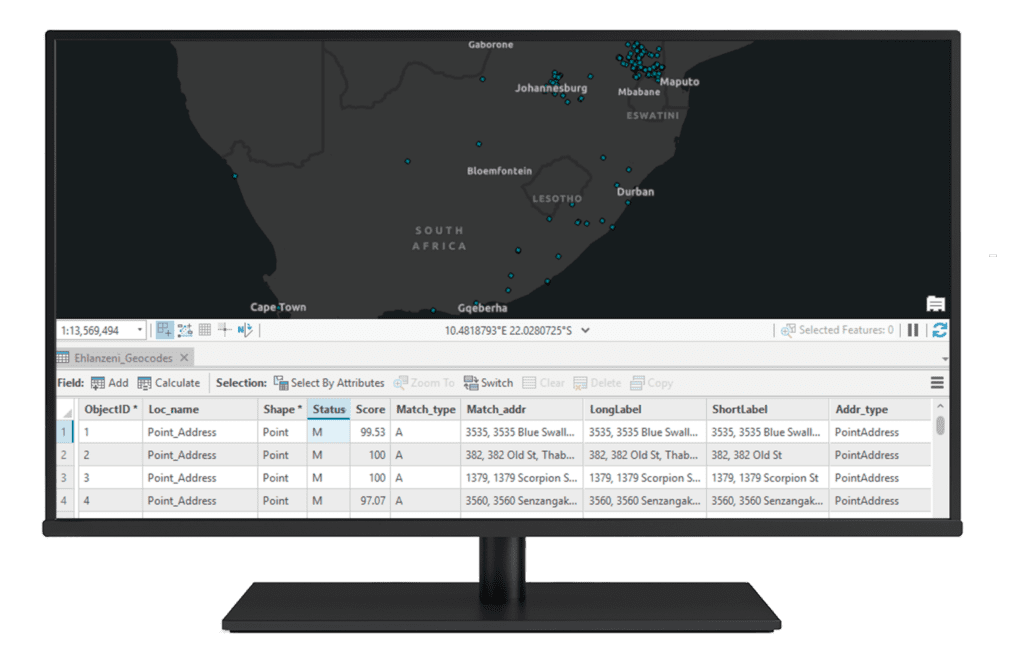
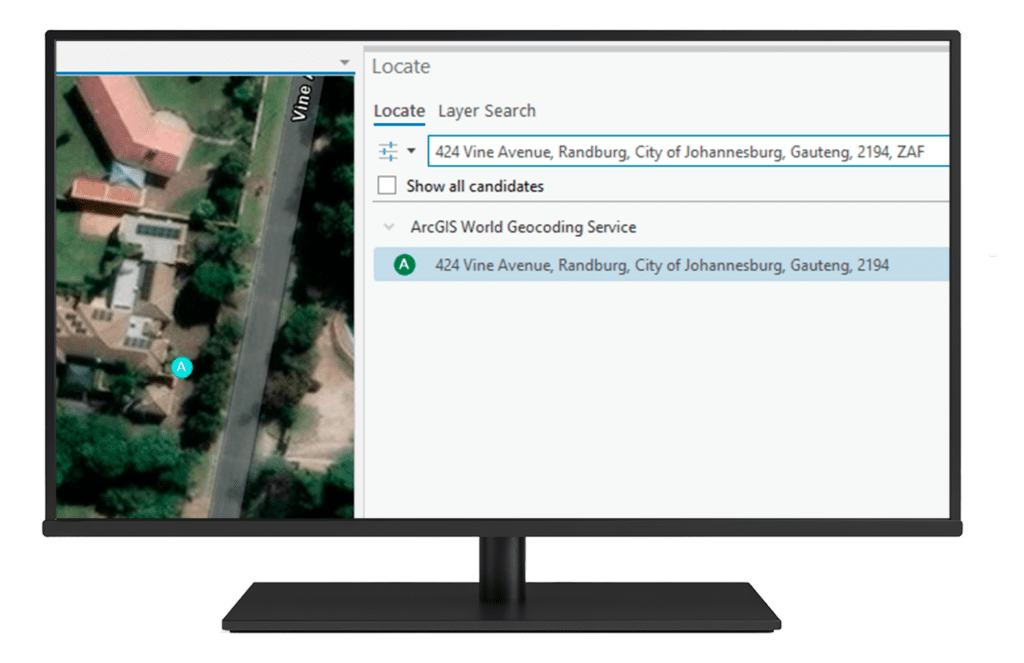
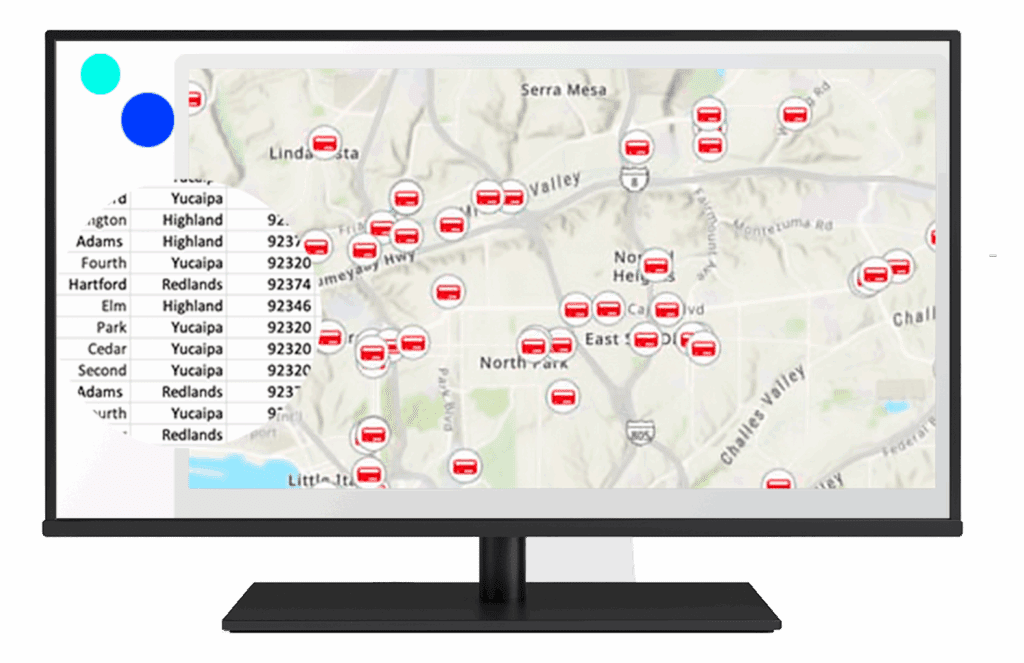
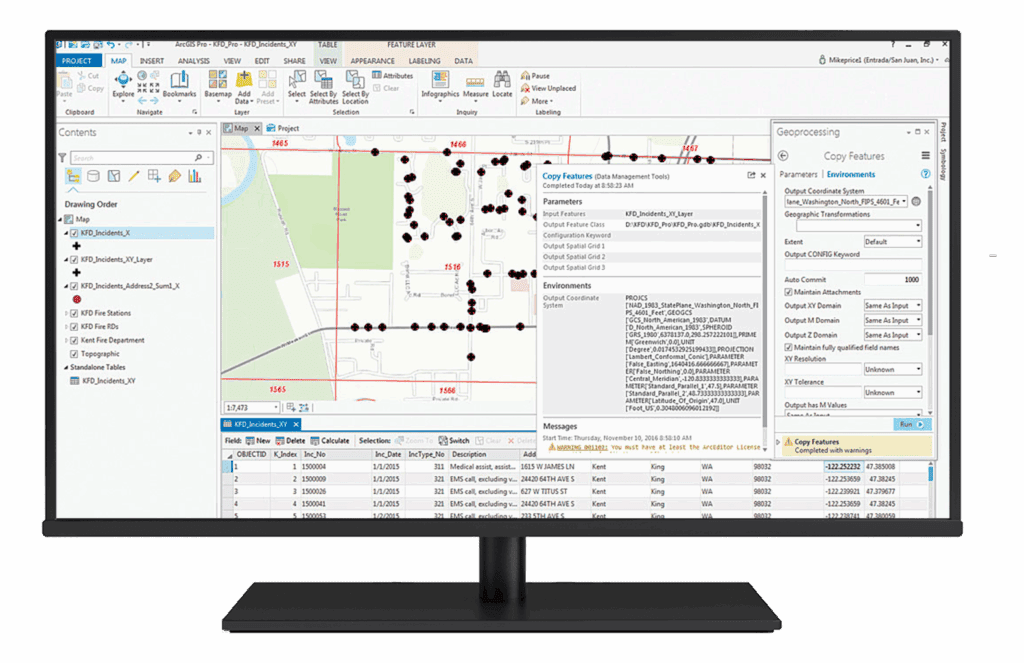
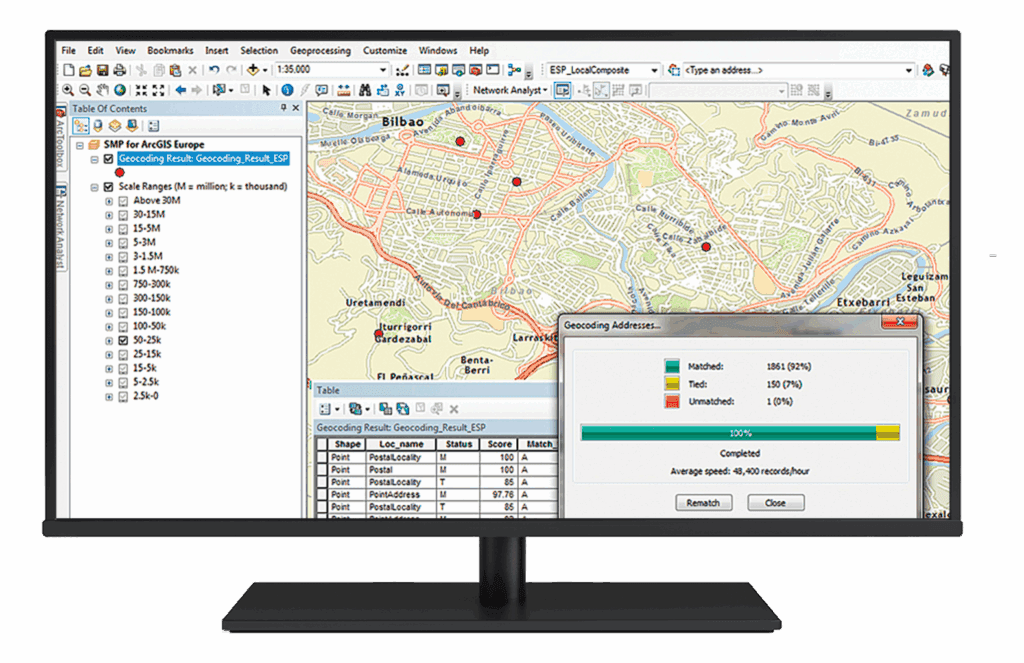
A complete geocoding solution efficiently converts address data into geographic coordinates, enabling businesses to visualize and analyse locations on maps. Using tools like Esri’s ArcGIS software, the process involves data collection, geocoding, quality control, and integration with GIS platforms for advanced analysis.
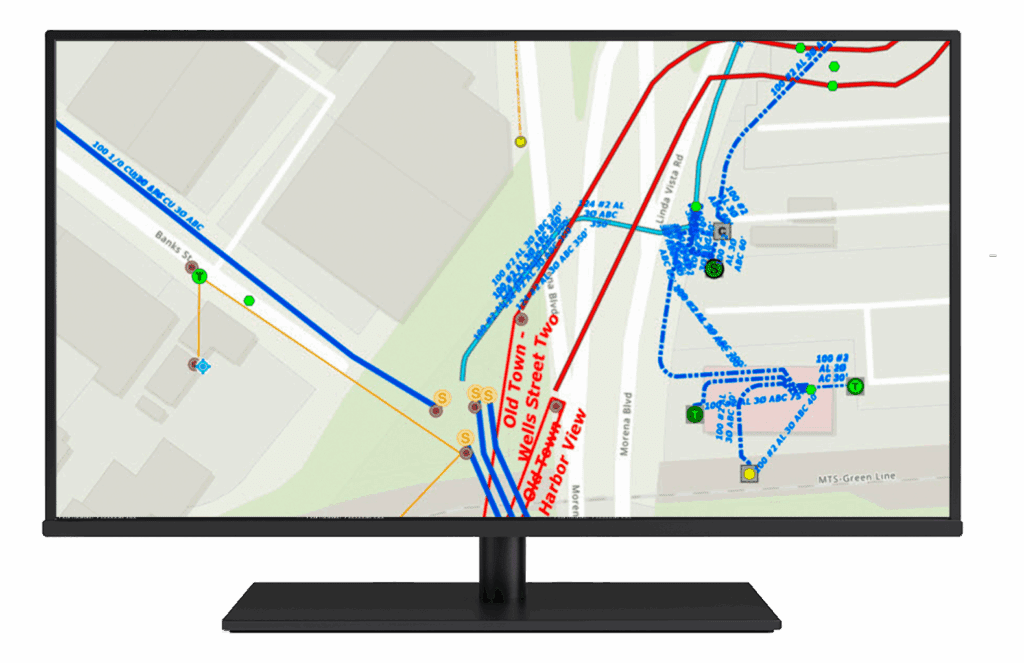
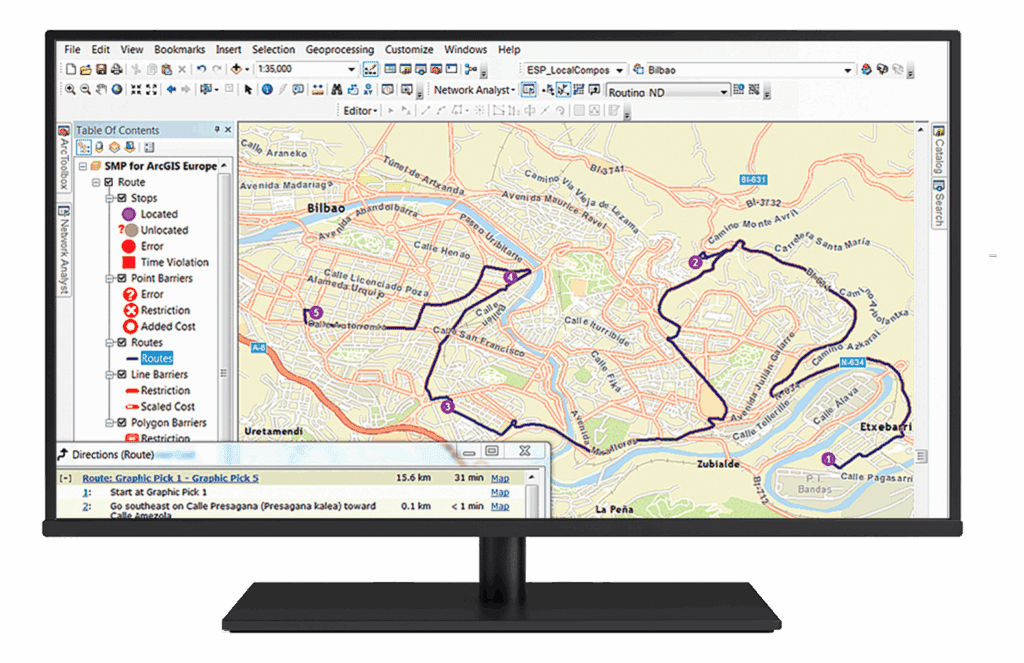
This solution supports batch geocoding, reverse geocoding, proximity analysis, and route optimisation, providing valuable insights for decision-making. It enhances operational efficiency by visualising spatial relationships, optimising logistics, and improving customer targeting, all while enabling collaboration to ensure data accuracy and relevance.
Geocoding as a solution
A complete geocoding solution efficiently converts address data into geographic coordinates, enabling businesses to visualise and analyse locations on maps. Using tools like Esri’s ArcGIS software, the process involves data collection, geocoding, quality control, and integration with GIS platforms for advanced analysis.









